Introduction
Biohazards are biological substances that pose a threat to the health of living organisms, particularly humans. Exposure to biohazards can occur in various settings such as laboratories, hospitals, sewage treatment facilities, and even natural environments. Proper protective gear is essential for anyone who may encounter biohazards to minimize the risk of infection or contamination. In this article, I will provide an in-depth overview of protective gear for biohazards, covering key types of equipment, materials, usage guidelines, and more.
Types of Biohazards
Some common biohazards include:
-
Infectious agents – Bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi that can cause diseases in humans. Examples are HIV, Hepatitis, Tuberculosis.
-
Toxins – Poisonous substances produced by living organisms. Examples are botulinum toxin, ricin, mycotoxins.
-
Laboratory samples – Tissues, blood, cells infected with infectious agents.
-
Medical waste – Needles, bandages, gloves from patient care.
-
Sewage – May contain bacteria, viruses, parasites from human waste.
Proper precautions are necessary when handling any materials that may contain these biohazards.
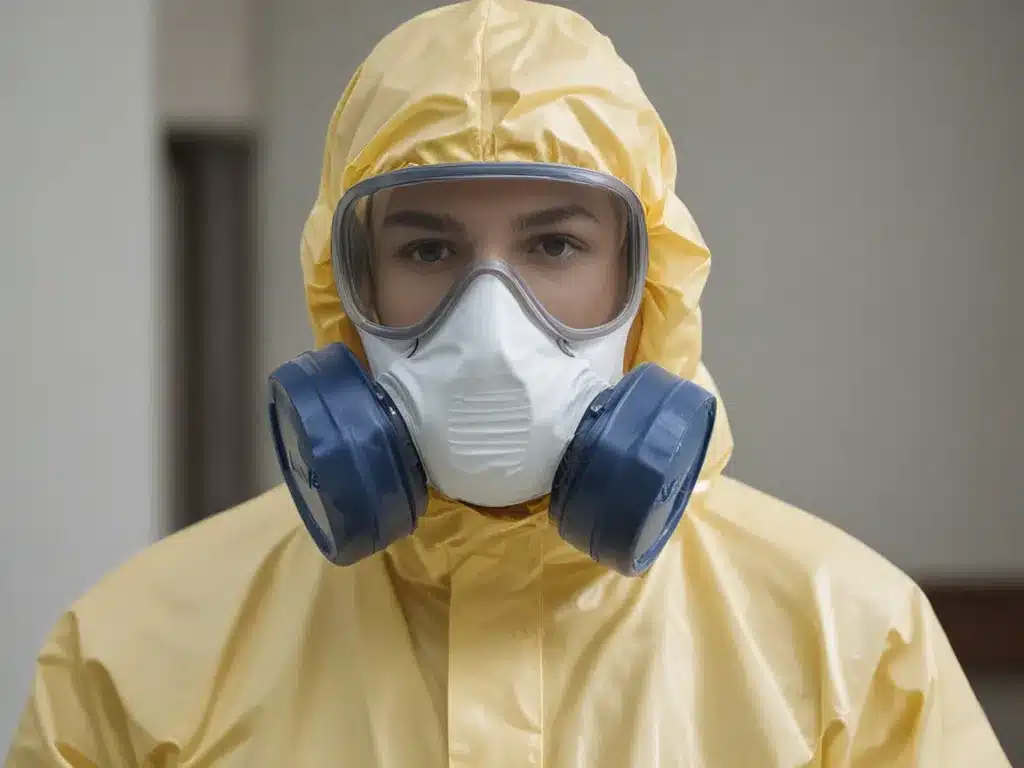
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
PPE creates a barrier between biohazards and your body. Main types of PPE for biohazards include:
Gowns and Coveralls
-
Full body coverage to protect skin and clothing from contact and splashes.
-
Made of materials like polypropylene which resists liquid penetration.
-
May be reusable or disposable. Reusables must be properly disinfected after each use.
Gloves
-
Protect hands from biohazard exposure.
-
Disposable latex, nitrile, and vinyl options available.
-
Reusable rubber gloves can also be used if properly sanitized.
-
Double gloving provides an extra layer of protection.
Eye Protection
-
Goggles or face shields guard eyes against splashes or airborne material.
-
Must have solid side shields and fit snugly to face.
Respirators and Masks
-
Respirators with correct filters block inhalation of airborne particles.
-
Surgical masks help block large droplets and splashes.
-
Proper fit and seal are essential for effectiveness.
Shoe and Boot Covers
-
Coverings for shoes or boots prevent contamination of footwear.
-
Can be made of polypropylene, polyethylene, or other liquids-resistant materials.
-
Disposable or reusable options available.
Head Covers
-
Hats, hoods, hairnets prevent contamination of hair and head.
-
Disposable options commonly used.
-
Some hoods are integrated with coveralls or gowns.
Using PPE Correctly
To get full protection from PPE, it must be used properly:
-
Inspect for defects before each use.
-
Select the right PPE for the biohazard risk.
-
Don and doff PPE in the proper sequence to avoid contamination.
-
Ensure proper fit. Gowns and coveralls should not be too loose or tight.
-
Practice correct removal and disposal to avoid touching contaminated surfaces.
-
Disinfect and maintain reusable items after each use.
-
Store PPE properly in clean area when not in use.
-
Change when PPE becomes heavily contaminated.
-
Do not reuse disposable PPE.
Proper training and practice are essential to use PPE correctly. Always follow manufacturer guidelines.
Specialized PPE
For handling high-risk biohazards, more extensive PPE may be needed:
-
Encapsulating suits – Whole body suits with breathing apparatus for hazardous materials emergency response.
-
Powered air purifying respirators (PAPRs) – Use battery-powered blowers and high-efficiency filters for added protection compared to ordinary respirators.
-
Self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA) – Provide clean air supply from oxygen tank for use in environments with hazardous gases or oxygen-deficiency.
Proper training is critical for using these advanced PPE systems safely.
Facility and Equipment Decontamination
Thorough decontamination of facilities and equipment is also vital when handling biohazards:
-
Use EPA-registered disinfectants effective against biohazards present.
-
Frequent surface cleaning and proper waste disposal protocols must be implemented.
-
HEPA filtration systems can filter airborne particles.
-
Tools and equipment used must be sterilized after use.
-
Facility design should allow for separate clean and contaminated zones.
Proper decontamination protects workers as they move between areas and prevents release of pathogens.
Conclusion
Working with biohazards presents unique health risks. Wearing the proper protective gear and using it correctly is the first line of defense when handling potential exposure situations. The appropriate PPE and decontamination procedures depend on the specific biohazard. With suitable precautions and training, the risks posed by these hazards can be minimized. Proper use of protective gear is essential for anyone who may encounter biohazards at work.