Introduction
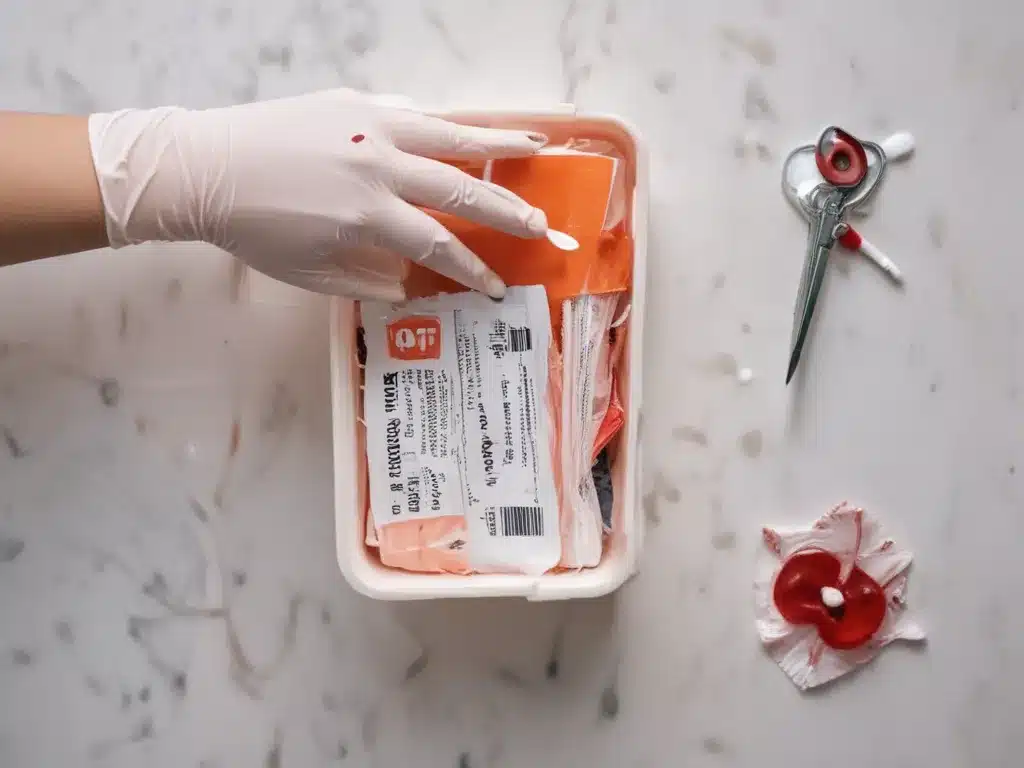
Proper medical sharps disposal is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and healthy environment in healthcare facilities, homes, and workplaces. Medical sharps, which include needles, syringes, lancets, and other sharp instruments used in medical procedures, can pose significant risks if not handled and disposed of correctly. Improper disposal can lead to accidental needle-stick injuries, potentially exposing individuals to bloodborne pathogens such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV. In this comprehensive article, we will explore the importance of proper medical sharps disposal, the regulations and guidelines surrounding it, and the best practices for safe handling and disposal.
What are Medical Sharps?
Medical sharps refer to any device or object that has the potential to puncture or lacerate the skin. These include:
- Needles (hypodermic, suture, and other types)
- Syringes with attached needles
- Lancets (used for finger-stick procedures)
- Scalpels
- Glass pipettes
- Broken glass from medical equipment
These sharps are commonly used in various medical settings, such as hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and even in home healthcare scenarios for individuals who require self-administered injections or blood glucose monitoring.
Risks Associated with Improper Disposal
Improper disposal of medical sharps can pose significant risks to healthcare workers, patients, and the general public. These risks include:
-
Needle-stick injuries: Needle-stick injuries can occur when sharps are not properly disposed of, potentially exposing individuals to bloodborne pathogens.
-
Infection transmission: Used sharps can transmit diseases such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV if they come into contact with an open wound or mucous membrane.
-
Environmental contamination: Improperly discarded sharps can end up in landfills, waterways, or public areas, posing a risk to wildlife and the general public.
-
Legal liabilities: Failure to comply with proper disposal regulations can result in fines and legal consequences for healthcare facilities and individuals.
Regulations and Guidelines
To mitigate the risks associated with medical sharps disposal, various regulations and guidelines have been established by government agencies and professional organizations. Some of the primary regulations and guidelines include:
-
Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA): OSHA’s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard (29 CFR 1910.1030) outlines specific requirements for the handling and disposal of sharps in healthcare settings.
-
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA): The EPA’s Medical Waste Tracking Act and Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) provide guidelines for the proper management and disposal of medical waste, including sharps.
-
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): The CDC provides comprehensive guidelines for the safe handling and disposal of medical sharps, including recommendations for labeling, containerization, and transportation.
-
State and local regulations: Many states and local municipalities have additional regulations and requirements for medical sharps disposal that must be followed.
Safe Handling and Disposal Practices
To ensure the safe handling and disposal of medical sharps, the following best practices should be followed:
1. Containerization
- Use puncture-resistant, leak-proof containers specifically designed for sharps disposal.
- Clearly label the containers with the appropriate biohazard symbol.
- Do not overfill containers, as this can increase the risk of needle-stick injuries.
2. Handling and Transportation
- Never recap, bend, or break used needles.
- Use tongs or forceps to handle sharps whenever possible.
- Transport sharps containers securely and in an upright position to prevent spills.
3. Disposal Methods
- Approved disposal methods vary depending on the type of facility and local regulations.
- Common disposal methods include:
- Mail-back programs
- On-site autoclaving or incineration
- Use of licensed medical waste disposal companies
4. Training and Education
- Provide ongoing training and education to healthcare workers, patients, and caregivers on proper sharps handling and disposal procedures.
- Emphasize the importance of following safety protocols and the potential risks associated with improper disposal.
5. Needle-stick Injury Response
- Have a clear protocol in place for responding to needle-stick injuries, including immediate first aid, reporting procedures, and follow-up care.
- Encourage prompt reporting of any needle-stick incidents to facilitate appropriate medical treatment and reduce the risk of infection transmission.
Case Study: The Importance of Proper Sharps Disposal
To highlight the significance of proper medical sharps disposal, let’s consider a real-life case study:
In 2018, a beach in New Jersey was temporarily closed after several used syringes washed ashore. This incident not only posed a potential health hazard to beachgoers but also raised concerns about the environmental impact of improperly discarded medical waste.
Investigations revealed that the syringes likely originated from a nearby hospital or healthcare facility, where improper disposal practices had allowed the sharps to enter the waste stream and ultimately end up in the ocean.
This case study serves as a stark reminder of the far-reaching consequences of inadequate sharps disposal practices. It underscores the importance of adhering to proper protocols and regulations to protect public health, the environment, and the safety of all individuals.
Conclusion
Proper medical sharps disposal is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and healthy environment. By following regulations, guidelines, and best practices, healthcare facilities, individuals, and communities can minimize the risks associated with needle-stick injuries and the transmission of bloodborne pathogens. It is essential to prioritize ongoing education, training, and adherence to established protocols to ensure the safe handling and disposal of medical sharps. Remember, taking the time to properly dispose of sharps is a responsibility we all share, and it can make a significant difference in protecting lives and preserving our environment.