What are bed bugs?
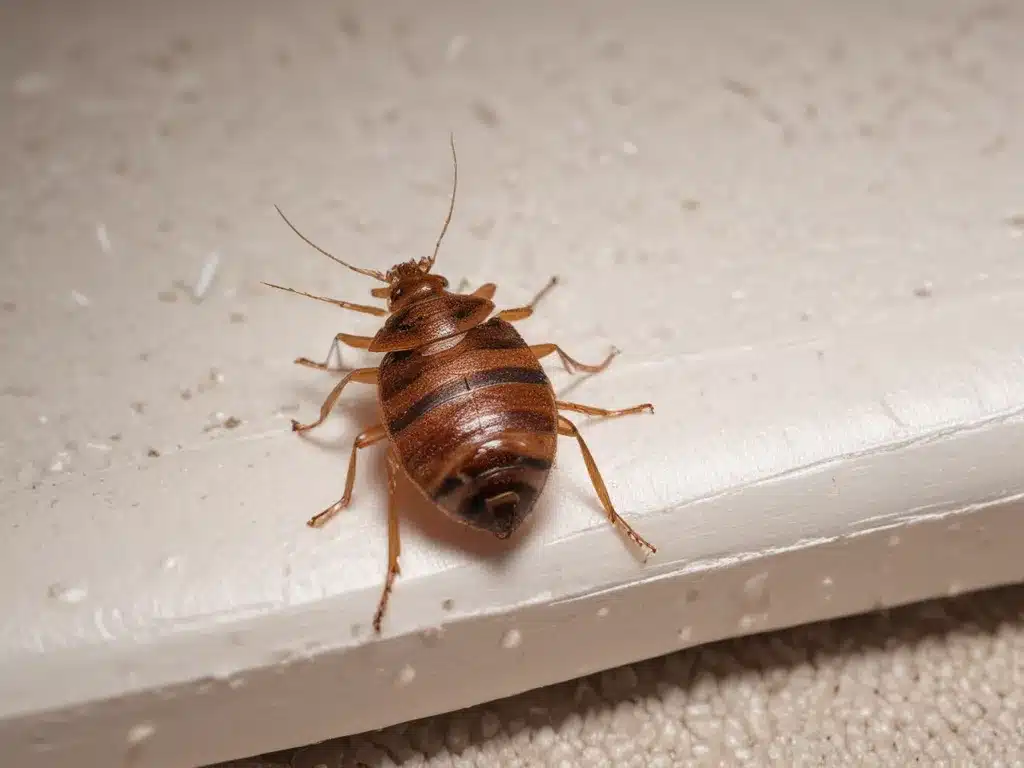
Bed bugs (Cimex lectularius) are small, flat, parasitic insects that feed exclusively on blood. They are reddish-brown in color and about the size of an apple seed as adults. Bed bugs are active at night and bite exposed areas of skin, such as the face, neck, arms, and hands while people sleep. The bites cannot be felt initially but may develop into itchy welts or swelling the following day.
Bed bugs can be difficult to detect due to their small size and ability to hide in cracks and crevices. They can travel from place to place by clinging onto clothing, luggage, furniture, bedding, and more. Infestations often arise after bringing in used furniture or after staying in an infested environment like a hotel room.
Signs of a bed bug infestation
Here are some common signs that may indicate the presence of bed bugs:
-
Bites – Small, itchy, red welts on exposed skin, often in linear patterns of 3 or more. Bites may take a day or two to become noticeable.
-
Blood stains – Small dark spots on bed sheets and mattresses from crushed bugs.
-
Odor – Some describe the smell as sweet or musty. Large infestations can create an unpleasant odor.
-
Cast skins – Light brown shells bed bugs leave behind after molting.
-
Live bugs – The best indication is visually spotting the bugs, especially around mattress seams and edges. They can be difficult to find due to their size and ability to hide.
Where do bed bugs hide?
Bed bugs prefer cracks, crevices, and other hidden locations that provide shelter and access to hosts. Common areas to inspect include:
-
Mattress seams and edges – Favorite spots are fabric piping and tags.
-
Bed frames – Especially wood frames with cracks and joints.
-
Headboards – Behind loose fabric and wood crevices.
-
Near bedding – Under the corners of sheets, pillowcases, and mattress covers.
-
Furniture – Under cushions, seams, and upholstered surfaces. Inside drawers and cabinets.
-
Baseboards and flooring – Cracks where walls meet floors offer excellent harborages.
-
Clutter – Areas with papers, books, toys and other items make it easier for bugs to remain hidden.
How to prevent bed bug infestations
Here are some tips to help prevent bringing bed bugs into your home:
-
Inspect secondhand furniture – Check all used beds, couches and other upholstered items for signs of bugs before bringing them home.
-
Use mattress encasements – Zippered covers that fully enclose mattresses can trap bugs and make detection easier.
-
Reduce clutter – Get rid of excess papers, boxes and other items bugs can hide in.
-
Inspect after traveling – Thoroughly check luggage and clothing after staying in a hotel or another person’s home.
-
Isolate and wash items after returning – Place clothing and luggage in sealed bags until they can be washed and dried on high heat.
-
Seal cracks and crevices – Caulk and repair openings wherever possible to limit potential harborages.
Professional bed bug treatment options
If bed bugs are detected, professional pest control is highly recommended. Treatment typically involves:
-
Inspection – All beds, furniture and harborages will be checked to locate bugs.
-
Steam cleaning and vacuuming – Physical removal and heat treatment kills bugs on contact.
-
Insecticide applications – EPA-registered products for indoor bug control will be sprayed into cracks, crevices, and key areas.
-
Non-chemical options – Some companies use heat chambers or freezing methods to kill bugs without insecticides.
-
Follow-up visits – Additional treatments are usually needed after the initial service to kill newly hatched bugs.
Successful elimination requires an accredited pest professional, cooperation from the home’s occupants, and patience while repeat visits occur over weeks or months.
DIY bed bug treatment options
For minor infestations, some people attempt do-it-yourself treatments. Common methods include:
-
Mattress encasements – Placing a quality, bed bug-proof cover over the mattress traps bugs inside and makes detection easier.
-
Thorough cleaning – Scrubbing and vacuuming cracks and crevices removes bed bugs and eggs on contact. Steam cleaners help reach into hidden areas.
-
Traps and monitors – Special traps can catch and reveal bed bugs. Double-sided tape under furniture also captures wandering bugs.
-
Sprays and dusts – Insecticides approved for indoor use can be applied into harborage areas and entry points, but may have limited effectiveness alone.
-
Heat treatment – Portable heaters brought into infested rooms can raise temperatures high enough to kill bugs and eggs.
-
Cold treatment – Some people have success placing small infested items in below freezing temperatures for at least 4 days.
For serious infestations, DIY treatment is often inadequate and runs the risk of scattering bugs to other rooms. Calling in a pest control professional is highly advised in most situations.