Introduction
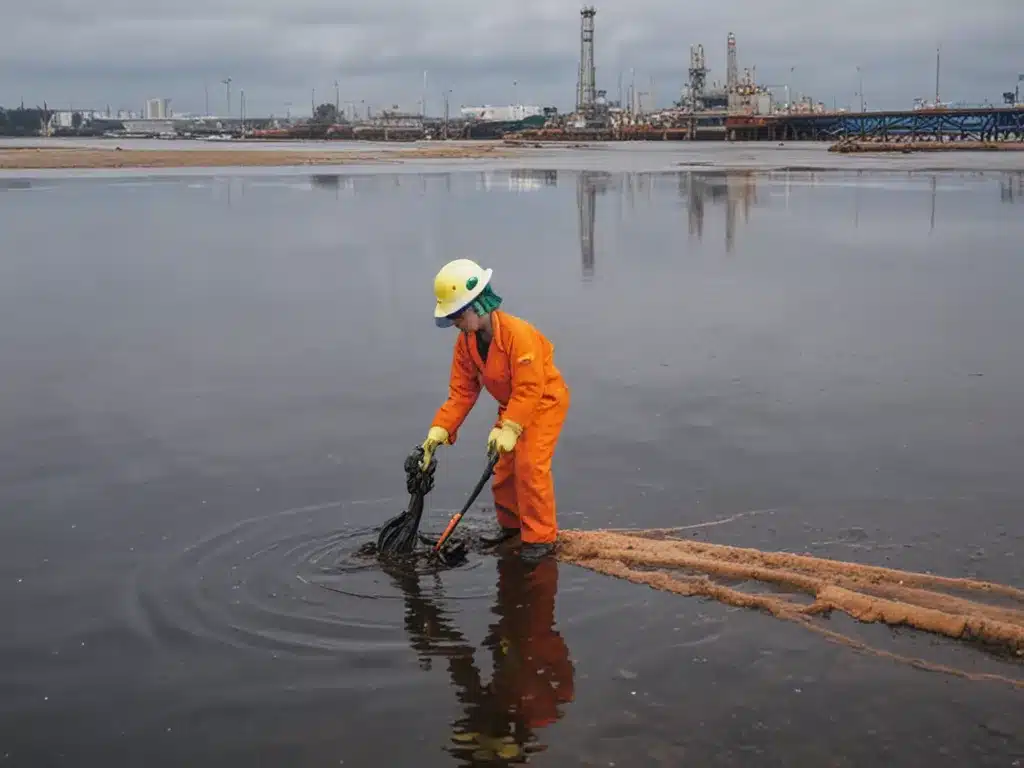
Chemical and oil spills can be extremely hazardous, and knowing how to handle them safely is critical. As someone who frequently works with chemicals and oils, I want to share some of my top tips for safe spill handling and cleanup. Properly handling spills helps protect health, the environment, and facilities.
Preparation is Key
The best way to handle a chemical or oil spill is to be prepared before one even occurs. Here are some key ways to get ready:
-
Have a written emergency response plan. Make sure all staff know procedures, roles, and responsibilities in the event of a spill. Include contact information for supervisors, cleanup crews, and regulatory agencies.
-
Train employees. Educate staff on proper spill prevention, containment, cleanup, and disposal techniques. Conduct annual refresher training.
-
Have spill kits stocked and accessible. Commercial spill kits contain absorbents like pads, booms, and loose absorbent material. Also stock PPE like gloves, goggles, masks, and chemical-resistant clothing.
-
Know your facility. Identify high-risk areas, drainage systems, water bodies, and more that could be impacted. This helps with quick, targeted responses.
Spill Containment
When a spill does occur, following proper containment steps is crucial:
-
Act quickly. Limit the spill’s spread by promptly shutting valves, plugging leaks, and uprighting overturned containers. Timeliness is key to minimizing contamination.
-
Wear PPE. Don respirators, gloves, goggles, and protective clothing appropriate for the type of chemical spilled before approaching.
-
Stop the flow. Prevent spills from entering drains, sewers, streams, or soil. Use absorbents to create barriers and contain the spill.
-
Notify supervisors. Report all spill incidents per workplace procedures so proper teams can coordinate responses.
-
Isolate hazards. Rope off spill sites and post warning signs to prevent unauthorized access.
Spill Cleanup
With the spill contained, carefully proceed with cleanup:
-
Determine risks. Identify the substance spilled and associated hazards like flammability, reactivity, and toxicity. Refer to Safety Data Sheets.
-
Select PPE. Choose protective gear suitable for the chemical and amount spilled. More hazardous materials warrant more robust PPE like fully encapsulated suits.
-
Absorb spill. Apply appropriate absorbent pads, booms, or loose materials over the entirety of the spill. Absorbents lock in liquids.
-
Containerize. Carefully shovel or sweep up spent absorbents and transfer to labeled drums or buckets for disposal.
-
Decontaminate. Wash spill site surfaces thoroughly using detergent or other appropriate cleaners.
-
Ventilate area. Increase air circulation and exchange to reduce vapors.
-
Dispose properly. Follow all applicable hazardous waste regulations when disposing of spill cleanup materials.
Special Considerations
Certain spill situations require extra precautions:
-
For large spills, coordinate response efforts with emergency crews and regulatory agencies. You may need special tools, equipment, and tactics.
-
With flammable material spills, eliminate all nearby ignition sources and use spark-proof cleanup tools. Monitor air concentrations.
-
For spills entering drains/sewers, try to seal off entryways. Retrieving chemicals from inside drains can be very challenging.
-
Outdoor spills require barriers to prevent environmental contamination of soil and waterways.
The Bottom Line
While chemical and oil spills must be taken seriously, following safe handling and cleanup best practices helps ensure minimal impacts on health, facilities, and the environment. Take time to properly prepare response plans and equipment ahead of any accidents.